Power outages are more than just an inconvenience; they're disruptive, potentially dangerous, and can lead to significant financial losses. In an increasingly connected world, where our homes are hubs for work, school, entertainment, and even medical care, losing power means losing control. That's why Selecting the Right Generator & Connection System for Your Home isn't just a luxury—it's a critical decision for modern homeowners seeking true peace of mind.
This guide is for you if you're ready to take charge of your home's power future. We'll cut through the jargon and empower you with the knowledge to choose a backup power solution that truly fits your needs, ensuring your household never misses a beat when the grid falters.
At a Glance: Your Generator Selection Checklist
- Prioritize Power Needs: Decide if you need partial home backup (essentials) or whole-home coverage.
- Evaluate Fuel Types: Natural gas offers unlimited runtime, propane is flexible, and diesel is robust for heavy loads.
- Calculate Your Wattage: Account for both running and surge wattage of critical appliances. Don't guess!
- Invest in Professional Installation: Safety, compliance, and optimal performance depend on it.
- Plan for Maintenance: Generators are like cars—they need routine service to be reliable.
- Standby is Key: For automatic, seamless power restoration, a permanently installed standby generator is the superior choice over portables.
The Unseen Threat: Why Every Home Needs a Backup Plan
Imagine this: a winter storm knocks out power for days. Your pipes freeze, the food in your fridge spoils, and your family huddles in the cold. Or perhaps it's a sweltering summer, and without air conditioning, your home becomes unbearable, not to mention the risk to sensitive medical equipment. These aren't hypothetical scenarios; they're common realities faced by homeowners every year.
Modern homes rely on a constant flow of electricity for virtually everything: climate control, refrigeration, lighting, communication, security systems, and increasingly, medical devices and remote work infrastructure. When the power grid falters, whether due to severe weather, equipment failure, or unexpected demand surges, the impact on daily life is immediate and profound. A reliable backup generator acts as your home's insurance policy, stepping in automatically to restore comfort, safety, and functionality when the lights go out. It's about protecting your investment, your family's well-being, and your ability to live life uninterrupted.
Your First Step: Defining Your Home's Power Priorities
Before you even start looking at generator models, the most crucial decision you'll make is determining what you absolutely need to power during an outage. This isn't just about personal preference; it directly impacts the size of the generator you'll need and, by extension, the overall cost.
Partial Home Backup: Essentials for Peace of Mind
For many households, especially those in areas with relatively short or infrequent outages, powering just the essentials is a smart and budget-friendly approach. This strategy focuses on keeping critical systems running, preventing major disruptions and costly damage.
Think about what truly matters:
- Food Preservation: Your refrigerator and freezer are paramount to avoid spoilage.
- Safety & Comfort: Lights, Wi-Fi for communication, a sump pump to prevent flooding, and perhaps a well pump for water supply.
- Basic Climate Control: A furnace fan to circulate heat in winter or a small window AC unit for critical rooms in summer.
A partial home backup system ensures you can weather an outage comfortably without needing to run every single appliance in your home. It's a practical choice for maintaining core functions and keeping your family safe and connected.
Whole-Home Coverage: Uninterrupted Living
If you live in an area prone to extended outages, rely heavily on medical equipment, or simply want the ultimate peace of mind, whole-home coverage is the answer. This option ensures your home operates almost identically to how it would with utility power.
With whole-home coverage, you can expect:
- Full HVAC Functionality: Maintaining comfortable temperatures throughout your entire house.
- Complete Kitchen Use: Running your oven, microwave, dishwasher, and all major appliances.
- Uninterrupted Daily Life: Powering laundry machines, multiple TVs, home office setups, and all lighting circuits.
These systems are typically permanently installed, automatically sensing an outage and seamlessly transferring power. It's the most robust solution, designed for households where any interruption to modern conveniences is simply not an option.
Fueling Your Home: Understanding Generator Options
The type of fuel your generator uses is a fundamental decision, impacting everything from installation to runtime and environmental considerations. Each option has distinct advantages tailored to different needs and resources.
Natural Gas: The "Set It and Forget It" Choice
Natural gas generators are a popular choice for homeowners who prioritize convenience and extended runtime. They connect directly to your home's existing natural gas line, providing a virtually endless supply of fuel.
The Upsides:
- Constant Fuel Source: As long as your natural gas utility is operational, your generator will keep running. No need for manual refueling or worrying about fuel delivery during an emergency.
- Minimal Maintenance: Generally, natural gas units require less hands-on fuel management.
- Cleaner Emissions: Compared to diesel, natural gas burns cleaner, producing fewer emissions, which is a plus for environmental considerations and local air quality.
- Ideal for Long Outages: Their continuous fuel supply makes them perfect for prolonged grid failures.
Things to Consider: - Requires a natural gas line connection, which might necessitate professional plumbing work if one isn't readily available near the installation site.
- If a major earthquake or disaster disrupts the natural gas infrastructure, the generator will lose its fuel source.
Propane: Flexible and Reliable Power
Propane generators offer an excellent balance of reliability and flexibility, especially for homes where natural gas isn't an option or is less stable. They operate off an onsite propane tank, which can be sized to meet specific runtime requirements.
The Upsides:
- Long Shelf Life: Propane doesn't degrade over time, ensuring your stored fuel is ready when you need it.
- Cleaner Emissions: Like natural gas, propane burns cleaner than diesel, offering a more environmentally friendly footprint.
- Flexible Installation: Propane tanks can be installed above or underground, providing more options for placement.
- Reliable Performance: Known for consistent power output and good performance in various temperatures.
- Low Maintenance: Generally, propane generators are easy to maintain.
Things to Consider: - Relies on a finite fuel supply stored in a tank. The size of the tank directly impacts runtime, and you'll need to schedule refills.
- Fuel prices can fluctuate, and delivery might be challenging during widespread emergencies.
Diesel: Heavy-Duty Performance for Demanding Needs
Diesel generators are workhorses, often found in commercial settings but also a strong contender for large residential properties or homes with exceptionally high power demands. They are renowned for their efficiency and robustness.
The Upsides:
- High Efficiency for Heavy Loads: Diesel engines are incredibly efficient when under substantial load, making them cost-effective for high-demand applications.
- Durability and Longevity: Built to withstand continuous use and harsh conditions, offering a long operational lifespan.
- Reliable in Cold Weather: Diesel fuel performs well in colder temperatures, which is crucial for northern climates.
- Lower Fuel Consumption (under load): They tend to use less fuel per kilowatt-hour generated compared to other options when powering heavy appliances.
Things to Consider: - Diesel fuel can gell in extreme cold if not properly treated, requiring specific additives.
- Emissions are generally higher than natural gas or propane, though modern diesel generators are much cleaner than older models.
- Requires onsite fuel storage and regular refueling, similar to propane. Diesel fuel also needs to be "polished" or treated if stored for very long periods to prevent degradation.
Sizing It Right: How Much Power Do You Really Need?
This is where the rubber meets the road. Choosing the correct generator size, measured in watts, is paramount. An undersized generator won't power everything you need, while an oversized one is an unnecessary expense and less efficient.
Crunching the Numbers: Running vs. Surge Wattage
When calculating your power needs, you need to consider two key types of wattage:
- Running Wattage (Rated Wattage): This is the continuous power an appliance needs to operate.
- Surge Wattage (Starting Wattage): This is the extra burst of power many motor-driven appliances (like refrigerators, AC units, or well pumps) require for a few seconds to start up. This surge can be 2-3 times the running wattage. Your generator must be able to handle the highest simultaneous surge wattage of all items you want to run.
The Calculation Method:
- List Everything: Make a comprehensive list of every appliance, light, and system you want to power.
- Find Wattage: Look up the running and surge wattage for each item. This information is usually on the appliance's data plate, in its manual, or easily found online.
- Prioritize and Sum: Add up the running wattage for all items you want to operate simultaneously.
- Identify Max Surge: Find the single highest surge wattage among your prioritized appliances.
- Add Them Up: Your total required wattage is the sum of your total running wattage PLUS that single highest surge wattage.
- Example: If your total running wattage is 5,000 watts, and your refrigerator has the highest surge at 2,000 watts (while other items are already running), you need a generator capable of at least 7,000 watts.
Appliance Wattage: A Quick Reference Guide
To give you a rough idea, here are some common appliance wattages (these can vary widely by model and efficiency):
- Refrigerator: ~700 watts running, 2000-2200 watts surge
- Freezer: ~500 watts running, 1500-2000 watts surge
- Furnace Fan (gas furnace): ~1000 watts running, 2000-3000 watts surge
- Sump Pump: ~750–1500 watts running, 2000-3000 watts surge
- Central Air Conditioner (3-ton): ~3500-4000 watts running, 8000-10,000+ watts surge
- Electric Water Heater: ~4500 watts (no surge)
- Microwave: ~1000-1500 watts
- Well Pump: ~1000-2000 watts running, 3000-4000 watts surge
- Lights (LED): ~10-100 watts per fixture
- Computer/Monitor: ~100-300 watts
- Wi-Fi Router: ~10-20 watts
Generator Capacity Tiers: Finding Your Fit
Generator sizes are typically categorized by their continuous running wattage:
- 3,000–5,000 watts: Best for minimal essentials. Think lights, a refrigerator, your Wi-Fi router, and charging phones. Good for short, infrequent outages.
- 5,000–8,000 watts: Powers a more robust set of key systems, including the items above plus a sump pump, furnace fan, or perhaps a small window AC unit. This tier often handles partial home backup very well.
- 8,000–12,000 watts: Moves into more comprehensive partial home coverage. This capacity can generally handle multiple major appliances, a well pump, and a good portion of your home's lighting and outlets, often including a larger furnace or a small central AC unit.
- 12,000–22,000+ watts: These are the whole-home workhorses. They can comfortably power your entire home, including central air conditioning, electric water heaters, multiple kitchen appliances, and all your essential electronics simultaneously. These units are designed for uninterrupted living.
Pro Tip: Always factor in a little extra capacity. It's better to have a slightly oversized generator than one struggling to keep up.
Beyond the Box: The Critical Role of Professional Installation
You've chosen your generator, but the journey isn't over. A generator isn't a plug-and-play appliance; it's a complex electrical system that integrates with your home's main power supply. Professional installation is not just recommended, it's absolutely non-negotiable for safety, reliability, and code compliance. Trying to hook up a generator to your house yourself without proper expertise can lead to dangerous situations, including electrical fires, electrocution, or backfeeding electricity into the grid, which endangers utility workers.
Why DIY is Never an Option for Home Generators
The danger of improper generator installation, particularly backfeeding, is immense. When a generator sends power back into the utility grid, it can electrocute utility workers who believe a line is dead. This is why strict electrical codes and safety measures are in place. Furthermore, incorrect wiring can damage your home's electrical system, destroy appliances, or even lead to fires.
What Professional Installation Entails
A qualified, licensed installer will handle every critical step:
- Property Assessment and Load Analysis: They'll confirm your generator size is correct by conducting a detailed load analysis of your home. They'll also assess your property for the best, safest placement of the generator, considering fuel lines, electrical connections, and local regulations.
- Permits and Code Compliance: Generators involve electrical, fuel, and sometimes plumbing work, all of which require permits and must adhere to local and national building codes (like the National Electrical Code, or NEC). Your installer will secure these permits and ensure all work meets these stringent standards.
- Generator Pad and Unit Setup: A solid, level concrete pad must be poured to support the generator, which can weigh hundreds or even thousands of pounds. The generator unit is then secured to this pad.
- Fuel Line Installation: For natural gas or propane units, the installer will run and connect the appropriate fuel lines from your home's supply or the propane tank to the generator.
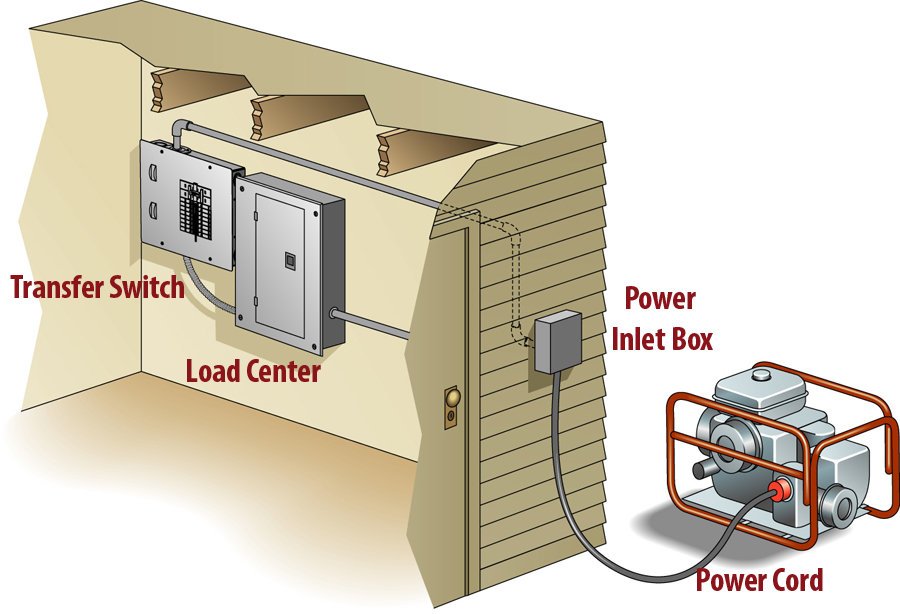
- Transfer Switch Installation: This is the heart of your home power integration. The transfer switch is installed between your home's main electrical panel and the utility meter. It safely disconnects your home from the utility grid before connecting it to the generator, preventing dangerous backfeeding.
- Electrical Wiring: All electrical connections between the generator, transfer switch, and your home's electrical panel are meticulously wired.
- System Testing: Once installed, the entire system is rigorously tested to ensure it activates automatically, transfers power correctly, and shuts down safely. This includes simulated power outages.
- Customer Walkthrough: Your installer will walk you through the system, explaining its operation, maintenance requirements, and safety protocols.
This comprehensive process ensures your generator is not only functional but also safe, reliable, and legally compliant.
The Brains Behind the Brawn: Understanding Transfer Switches
The transfer switch is the unsung hero of your home generator system. It's the critical component that distinguishes a safe, automatic backup power solution from a hazardous, manual one.
Essentially, a transfer switch performs two vital functions:
- Isolates Your Home from the Grid: When an outage occurs, it physically disconnects your home's electrical system from the utility company's lines. This prevents "backfeeding," where power from your generator could travel back into the grid and electrocute utility workers.
- Connects Your Home to the Generator: Once disconnected from the grid, it then connects your home's electrical system directly to the generator, allowing it to supply power safely.
There are two main types:
- Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS): This is standard for permanently installed standby generators. When the utility power fails, the ATS automatically senses the loss, starts the generator, and transfers the electrical load to generator power—all within seconds, with no action required from you. When utility power returns, it senses that too, transfers the load back, and shuts down the generator. This provides seamless, hands-off operation.
- Manual Transfer Switch (MTS): Primarily used with portable generators. An MTS allows you to manually switch your home's electrical load from utility power to a connected portable generator. While safer than extension cords, it still requires manual intervention and is not suitable for whole-home standby systems due to the lack of automation. For a deep dive into how to hook up a generator to your house safely, especially concerning transfer switches, consulting a professional is key.
For a standby generator, an automatic transfer switch is essential for achieving the "set it and forget it" reliability and convenience that makes these systems so valuable.
Keeping the Power On: Essential Generator Maintenance
A generator is an investment in your home's future, and like any critical piece of machinery, it needs regular care to perform optimally when you need it most. Neglecting maintenance is the fastest way to turn a reliable backup system into an expensive lawn ornament.
The Importance of Routine Care
Think of your generator as a car that sits in the garage 99% of the time, yet needs to start reliably and run perfectly at a moment's notice. Dust, moisture, temperature fluctuations, and simply the passage of time can all impact performance. Regular maintenance ensures:
- Reliable Startup: The battery is charged, fuel is clean, and spark plugs are ready.
- Peak Performance: The engine runs efficiently, delivering the power you need without strain.
- Extended Lifespan: Proper care prevents wear and tear, prolonging the life of your unit.
- Warranty Compliance: Most manufacturers require documented maintenance to keep your warranty valid.
What a Maintenance Plan Covers
Most standby generator systems require annual service or every 100–200 hours of use, whichever comes first. A typical maintenance plan from a certified technician includes:
- Oil and Filter Changes: Fresh oil and filters are vital for engine health.
- Battery Inspection and Testing: The battery is the heart of the starting system. It needs to be clean, charged, and in good condition.
- Spark Plug Inspection/Replacement: Ensures efficient combustion.
- Air Filter Replacement: Clean air is crucial for engine performance.
- Fuel System Inspection: Checking lines, connections, and ensuring fuel quality (especially for diesel).
- Valve Adjustment (if applicable): Maintains engine efficiency.
- Electrical System Check: Verifying all wiring and connections are secure and free of corrosion.
- Software Updates: Modern generators have sophisticated control boards that benefit from firmware updates.
- System Testing: Running the generator under load to confirm proper operation and power transfer.
- Visual Inspection: Checking for leaks, damage, or wear and tear.
Many generators have an automatic exercise cycle, where they run for a short period weekly or monthly to keep components lubricated and ensure readiness. However, this doesn't replace the need for professional annual service. For ongoing support and to truly understand your generator's connection to your house, regular professional check-ups are invaluable.
Why Make the Investment? The Unquantifiable Value of Standby Power
The cost of a generator can seem significant upfront, but the benefits it provides often far outweigh the initial investment, particularly when considering the true cost of an outage. Modern homes are intricately reliant on power, and a standby generator addresses this vulnerability directly.
- Seamless and Automatic Transition: Unlike portable units, standby generators kick in automatically, often within seconds. There's no fumbling in the dark, no extension cords, just continuous power.
- Protection Against Costly Damage: Prevents frozen pipes in winter, food spoilage in refrigerators and freezers, and sump pump failures that can lead to devastating basement flooding.
- Supports Modern Lifestyles: Ensures remote work, home schooling, and online communication remain uninterrupted.
- Safeguards Health and Well-being: Crucial for homes with medical equipment, oxygen concentrators, or mobility aids that require continuous power.
- Enhanced Safety: Permanently installed outside, they eliminate the carbon monoxide risks associated with portable generators used indoors.
- Whole-Home Comfort: Maintain HVAC, kitchen appliances, security systems, and all your creature comforts, preserving your family's quality of life.
- Increased Property Value: A professionally installed standby generator is a significant selling point, appealing to buyers looking for added security and convenience.
Ultimately, investing in a standby generator is investing in peace of mind. It's about knowing that no matter what the grid throws at you, your home remains a sanctuary of comfort, safety, and functionality.
Your Burning Questions: Generator FAQs Answered
We know you have questions, and we're here to provide clear, concise answers to some of the most common inquiries about home generators.
How much does a home generator installation typically cost?
Generator installation costs generally range from $5,000 to $15,000, but this is a broad estimate. The total cost varies significantly based on several factors: the size and brand of the generator, the fuel type (natural gas connections can involve more plumbing), local labor rates, the complexity of the installation site, and any required electrical upgrades or permits. Always get multiple detailed quotes from licensed professionals.
How long can a home generator run continuously?
The runtime largely depends on the fuel source:
- Natural Gas Units: Can run as long as your utility service is available, providing a continuous fuel supply.
- Propane and Diesel Generators: Typically run for 24–72 hours on a full tank, but this depends heavily on the size of your onsite fuel tank and the electrical load (how many appliances are running). Larger tanks mean longer runtimes between refills.
Can a generator truly power my entire house?
Yes, absolutely. With the right size and configuration, a generator can provide full-home coverage. This means powering everything from your central air conditioner and electric water heater to your kitchen appliances and all lighting circuits, allowing your home to operate almost seamlessly during an outage. This often requires generators in the 12,000–22,000+ watt range. Understanding how to connect a generator for whole-house power safely requires professional expertise.
What's the difference between a portable generator and a standby generator, and which is better? - Portable Generators: These are smaller, wheeled units that you manually start, refuel, and connect to specific appliances via extension cords, or to a manual transfer switch.
- Pros: Lower upfront cost, portable for camping or job sites.
- Cons: Manual setup, limited power output, shorter runtime (small fuel tank), significantly higher safety risks (carbon monoxide if used improperly), less efficient, requires constant monitoring and refueling.
- Standby Generators: These are permanently installed, larger units that automatically detect power outages, start themselves, transfer power to your home, and shut down when utility power returns.
- Pros: Automatic operation, greater reliability, longer runtime (often unlimited with natural gas), higher power output (can power whole home), enhanced safety (installed outdoors, no manual handling of fuel or electrical connections), quiet operation (often enclosed).
- Cons: Higher upfront cost, requires professional installation and maintenance.
Which is better? For home backup, standby generators are unequivocally superior due to their automatic operation, reliability, safety, and ability to power critical loads seamlessly. While portables have their niche, they cannot match the peace of mind and convenience of a standby system.
Taking the Next Step: Securing Your Home's Power Future
Selecting the right generator and connection system for your home is a decision that impacts your safety, comfort, and financial well-being for years to come. It's a significant investment, but one that pays dividends in peace of mind when the unexpected happens.
You now have a robust framework for understanding your power priorities, evaluating fuel options, accurately sizing your generator, and appreciating the critical role of professional installation and ongoing maintenance.
The next crucial step is to consult with licensed, reputable generator professionals in your area. They can perform a detailed load analysis for your specific home, recommend the ideal generator model and fuel type, provide accurate quotes, and ensure your system is installed safely and to code. Don't leave your family's safety and comfort to chance; empower your home with reliable backup power.